Have you ever wondered how your body maintains healthy hair, nails, and skin? Or how it converts the food you eat into energy? The answer lies in one vital nutrient: biotin. This vitamin H, often overlooked, plays a significant role in various bodily functions, making it essential for overall health. In this blog, we’ll dive deep into the function of biotin in the body, explore the benefits of biotin, and biotin dosage, and find ways to naturally boost your intake, whether through biotin foods or supplements.
Functions and Benefits of Biotin
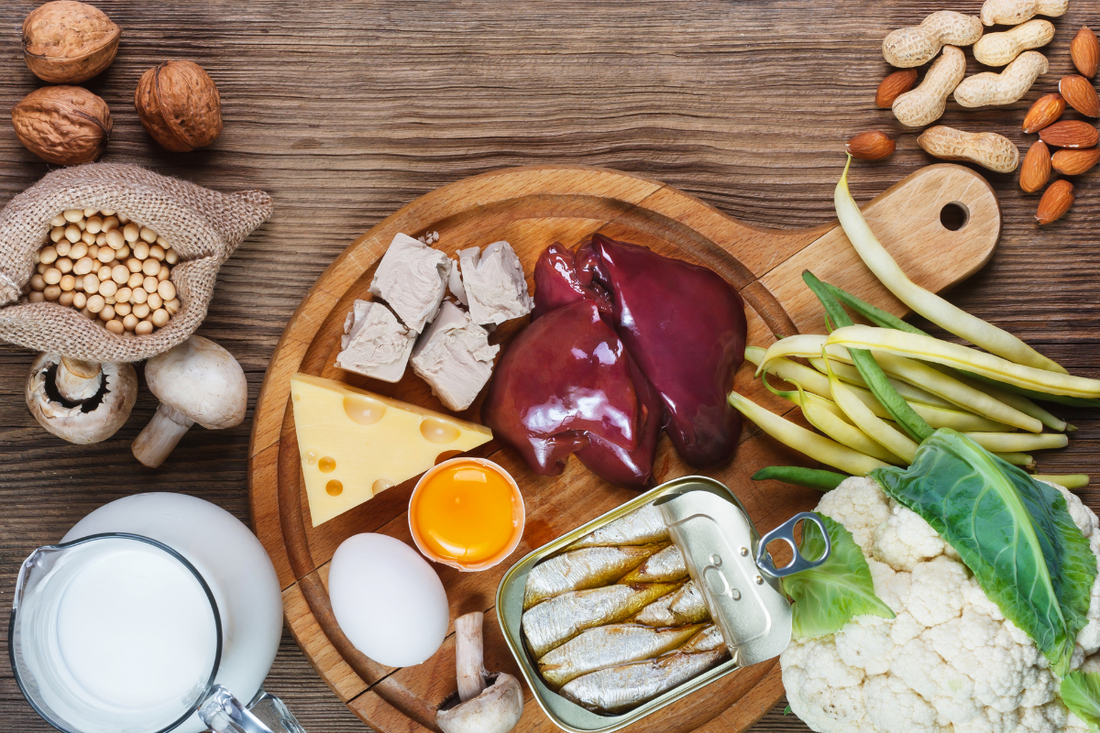
Biotin is a water-soluble vitamin, also known as vitamin B7 or H, that aids in multiple critical processes. Let’s explore the top five functions and benefits that biotin offers:
1. Supports Metabolism and Energy Production
One of the most essential functions of biotin in the body is its role in metabolism. Biotin acts as a coenzyme for carboxylase enzymes, which are crucial in the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into energy. It helps convert these macronutrients into fuel, ensuring that your body has the energy it needs for daily functions. Without sufficient biotin dosage, your body may struggle to efficiently use the food you eat for energy, leading to fatigue and other issues.
2. Promotes Healthy Hair, Skin, and Nails
Biotin has earned its reputation as the "beauty vitamin" due to its direct influence on the health of your hair, skin, and nails. People experiencing thinning hair or brittle nails are often dealing with a deficiency of biotin. Many studies suggest that regular intake of biotin can help strengthen hair, reduce hair fall, and improve nail thickness. Additionally, biotin helps maintain the hydration and overall health of the skin, making it essential for those looking to enhance their appearance naturally.
3. Essential for Pregnancy and Fetal Development
For expectant mothers, biotin becomes even more critical. Pregnant women have an increased risk of biotin deficiency, which can negatively impact fetal development. Biotin supports embryonic growth by facilitating the transfer of nutrients to the developing baby. A biotin supplement may be necessary for pregnant women to meet their increased nutritional needs and ensure the health of both the mother and baby. Doctors usually recommend a higher biotin dosage during pregnancy to avoid complications related to deficiency.
4. Improves Cognitive Function and Mental Health
Your brain relies on biotin to function correctly. This vitamin supports the nervous system by assisting in the production of neurotransmitters, which regulate mood, memory, and other cognitive functions. Emerging research suggests that a deficiency of biotin might contribute to neurological issues such as depression, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating. Consuming adequate biotin foods or a biotin supplement can help enhance mental clarity, reduce brain fog, and improve overall brain function.
5. Helps Regulate Blood Sugar and Manage Diabetes
Biotin also plays a role in regulating blood sugar levels. Some research suggests that it can improve insulin sensitivity, which helps in managing diabetes and reducing blood sugar spikes after meals. It is especially effective when paired with other supplements like chromium. Though more studies are needed to fully understand its impact, biotin is considered beneficial for those looking to stabilise their blood sugar. Regular consumption of biotin food sources or taking the best biotin supplements can support blood sugar management over time.
Daily Biotin Intake for Men and Women
While biotin is crucial for various body functions, getting the right biotin dosage is key to reaping its benefits. According to dietary guidelines, the recommended daily intake of biotin varies by age and gender.
- Men: The general recommendation for men is around 30 micrograms per day. This amount supports metabolic processes, hair and skin health, and overall body functions.
- Women: For women, the recommended daily intake is also around 30 micrograms. However, during pregnancy, this increases to 35 micrograms to meet the body's additional demands.
- Children: For children and teens, the recommended intake ranges from 5-25 micrograms per day, depending on age.
While these numbers are helpful, people with certain medical conditions, such as biotin deficiency, or those seeking specific health improvements might benefit from adjusting their biotin dosage with the help of healthcare providers.
How to Eat a High Biotin Diet?
Incorporating biotin food sources into your daily diet is an excellent way to naturally increase your intake. While biotin is present in many foods, here are some top picks to include in your diet:
1. Eggs (Whole Eggs and Egg Yolk)
One of the most convenient and versatile biotin food sources is eggs. One day fresh eggs are rich in biotin, especially in the egg yolk. A single large egg contains about 10 micrograms of biotin, which is roughly a third of your daily requirement. Alongside biotin, eggs also provide a wealth of other nutrients, such as vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and essential amino acids that promote overall health. Opt for whole eggs to get the full nutritional benefits, or incorporate the egg whites in your meals for a protein-packed boost. The bright orange yolk of a farm-fresh egg is a visual indicator of high nutrient content.
2. Biotin Supplements
For individuals who struggle to meet their daily biotin needs through food alone, biotin supplements are a reliable option. These supplements come in various forms, such as tablets, gummies, or capsules, and can deliver a concentrated dose of biotin. When selecting the best biotin supplements, ensure they come from reputable sources and are third-party tested for quality and purity. Supplements can help prevent or address biotin deficiency quickly, especially for those with specific health conditions that reduce biotin absorption.
3. Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, walnuts, sunflower seeds, and other nuts and seeds are excellent sources of biotin. A quarter cup of sunflower seeds, for example, provides around 2.6 micrograms of biotin. These biotin rich foods are also loaded with healthy fats, fiber, and other vitamins, making them an ideal snack for overall health. Add them to salads, yogurt, or just eat them raw for a quick biotin boost.
4. Leafy Greens
Spinach, kale, and other leafy greens are another biotin-packed option. Spinach, in particular, contains about 7 micrograms of biotin per serving, alongside a wealth of other essential vitamins like iron, folate, and magnesium. Including more greens in your diet not only increases biotin intake but also contributes to your overall nutritional profile.
5. Legumes
Lentils, peas, and beans are good sources of biotin. They are also rich in protein and fibre, making them an excellent addition to a balanced diet. For example, one cup of cooked lentils offers around 6 micrograms of biotin. Adding legumes to your meals will help ensure that you're covering your biotin food sources naturally.
Conclusion
Understanding the function of biotin in the body can help you appreciate its role in keeping you healthy and vibrant. While deficiencies are rare, ensuring adequate biotin intake through a diet rich in biotin foods can provide long-term health benefits. Whether you're looking to improve your beauty routine, boost energy levels, or support brain health, biotin is an essential vitamin to include in your diet. Incorporating Eggoz eggs, particularly those with a bright orange yolk, and other biotin-rich foods will keep your daily biotin intake sufficient, while supplements can offer a convenient solution to addressing any deficiencies.