Key Facts:
- Vitamin E protects cell membranes from free radical damage and unstable chemicals associated with ageing and chronic diseases.
- Early detection and treatment are essential to prevent nerve injury that causes extremity numbness and tingling.
- People with Crohn's, cystic fibrosis, or liver diseases may need Vitamin E supplements.
- Enough Vitamin E intake protects neurones from oxidative damage.
- Prolonged deficiency may cause neurological problems such as ataxia and peripheral neuropathy, impairing coordination and balance.
- The Vitamin E RDA for adults is 15 mg per day, depending on age and gender.
What Is Vitamin E and Why Is It Important?
Vitamin E, a fat-soluble vitamin, is essential to health. One of the body's main antioxidants, it neutralises free radicals to avoid oxidative stress, which can damage cells and cause chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes.
This vitamin supports the formation and activation of immune cells, which fight infections and diseases, in addition to its antioxidant capabilities.
The Lancet reports that over 67% of the world's population lacks vitamin E.
Vitamin E protects nerve cells and supports nervous system function. It moisturises and protects skin, making it a popular skincare ingredient.
Understanding Vitamin E Deficiency
Conditions that limit fat absorption can cause vitamin E deficiency, which is rare in healthy people. Since Vitamin E is stored in adipose tissue and absorbed from dietary fat, fat metabolism disruptions can significantly lower Vitamin E levels.1. Muscle weakness
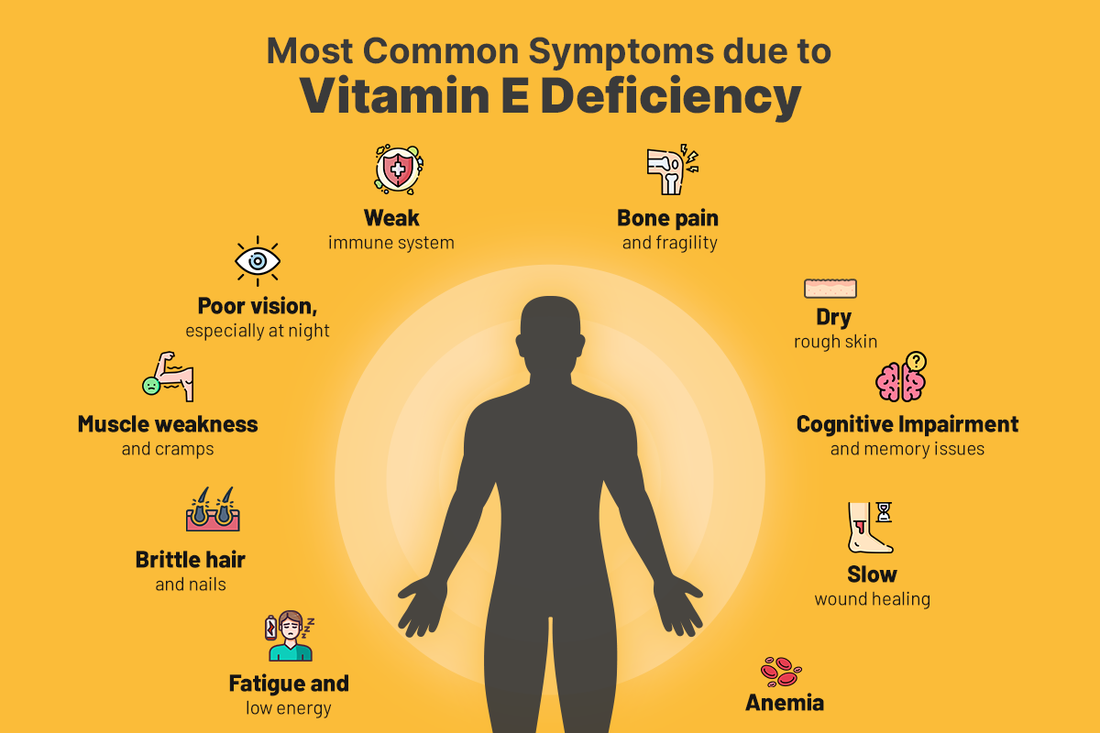
Vitamin E deficiency begins with muscle weakness. Vitamin E prevents muscle cell membrane oxidation. Without enough Vitamin E, these cells break down, diminishing muscle power and making jobs tougher. Time can affect mobility and quality of life.
2. Neurological Issues
Vitamin E needs the neurological system. Deficits can induce peripheral neuropathy, which destroys nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. Affected extremities may tingle, numb, or burn. Severe cases can impair reflexes and coordination, making daily tasks difficult.
3. Vision Problems
Vitamin E protects the retina from oxidation. Retinal function deficits can cause blurry vision, focus problems, and light sensitivity. These illnesses can cause irreversible vision loss or degenerative eye issues if untreated.
4. Immune System
Vitamin E enhances infection-fighting T-cells. Immune system weakness from Vitamin E deficiency makes humans more prone to sickness and infection.5. Balance and coordination issues
Vitamin E helps cerebellar motor control and coordination. Deficiency can cause ataxia, which impairs coordination, walking, and stability. This can restrict older people's freedom and safety.6. Anaemia
Vitamin E prevents oxidative damage in red blood cells. A deficiency can induce haemolytic anaemia, when red blood cells perish faster than they get replaced. Symptoms include fatigue, weakness, and pallor.7. Dry hair and skin
Vitamin E moisturises and protects skin. Deficits can produce dry, flaky skin and brittle hair as the body battles oxidative damage and hydrates cells.Vitamin-E-Rich Foods
Nutrient-rich diets help treat Vitamin E insufficiency. Certain foods are rich in vitamin E, making it accessible to most healthy eaters. Here are some good sources for everyday meals:
1. Seeds and nuts
Vitamin E-rich foods include almonds, sunflower seeds, hazelnuts, and peanuts. A single ounce of almonds contains 7.3 milligrammes of Vitamin E, about 50% of the RDA. More powerful sunflower seeds contain 12 mg of Vitamin E per quarter-cup. Eat a handful of these snacks to get Vitamin E, healthy fats, and proteins.
2. Oils
Vitamin E is highest in sunflower, safflower, and wheat germ oils. Wheat germ oil provides 20 mg of Vitamin E per tablespoon, more than most adults need. To maximise advantages, use these oils in salad dressings or low-heat cooking.
3. Leafy Greens
Vitamin E-rich plants include spinach, kale, Swiss chard and turnip greens. In one cup of cooked spinach, 4 milligrams of Vitamin E is found. Adding these vegetables to soups, stir-fries, or smoothies adds antioxidants and fibre.
4. Eggs
Each egg contains 1 mg of Vitamin E, making them a diverse and accessible source. Apart from Vitamin E, they provide high-quality protein, important amino acids, and brain-healthy choline. Add eggs to salads, breakfasts, and mains for a nutritious meal.
These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, preventing Vitamin E deficiency and improving general health.
Conclusion:
Vitamin E deficiency is treated by emphasising nutrition, addressing health conditions, and handling food safely. Preventing Vitamin E deficiency boosts immune, brain, and skin health. A balanced diet with Eggoz eggs and a healthy lifestyle requires knowledge, proactivity, and commitment. A happier, more vibrant existence starts with correcting nutritional inadequacies like Vitamin E inadequacy.